The Cisco 300-410 ENARSI exam continues to be one of the most valued certifications for advancing into mid-to-senior enterprise networking roles. As organizations shift toward fully automated, secure, and scalable hybrid networks, ENARSI-certified professionals are in high demand. In late 2025, Cisco updated the CCNP Enterprise track to better align with emerging architectures, making the current ENARSI exam even more relevant as we move toward 2026.
What the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI Exam Covers Today
Cisco’s 2025 blueprint confirms focuses on:
- Advanced routing implementation
- Layer 3 VPNs
- OSPF, EIGRP, BGP troubleshooting
- Infrastructure services (DHCP, NAT, SNMP, NTP)
- Secure network operations
These topics are expected to stay stable into 2026, though Cisco continues to emphasize automation and real-world troubleshooting.
Why Candidates Struggle With the 300-410 Exam
Many candidates underestimate the hands-on intensity. The exam isn’t just theory—it evaluates your ability to diagnose routing issues, interpret real-world logs, and apply configuration logic quickly. The pressure of simulation-style questions is a common challenge in the 300-410 exam.
How Updated Leads4pass 300-410 Dumps Can Help You
Updated dumps give candidates clarity on question patterns and complexity. Leads4pass provides both PDF and VCE practice formats, giving flexibility whether you study on desktop or mobile. Practicing with realistic scenarios improves speed and reinforces troubleshooting logic.
Where to Download the Latest Updated 300-410 Dumps
The newest version of the Leads4pass 300-410 dumps (955 Q&A) is available here:
👉 Latest 300-410 Dumps (https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html)
These align well with the 2025 exam structure and expected 2026 updates in routing, VPN, and advanced network operations.
How to Use 300-410 Dumps Effectively
Cisco 300-410 dumps should validate mastery, not replace study. Combine three pillars:
- Official Cisco documentation
- Hands-on labs
- Updated practice questions
Using 300-410 dumps only at the final phase is the most effective method for long-term skill development.
Latest Cisco CCNP Enterprise 300-410 dumps exam questions and answers
| Number of exam questions | Total Questions | Related certification materials |
| 15 (Free share) | 955 Q&A (From Leads4Pass) | CCNP |
Question 1:
An OSPF area contains the following networks:
165.164.8.0 255.255.254.0
165.164.10.0 255.255.254.0
165.164.12.0 255.255.254.0
165.164.14.0 255.255.254.0
How can the route to these networks be summarized?
A. 165.164.8.0 255.255.240.0
B. 165.164.8.0 255.255.248.0
C. 165.164.10.0 255.255.252.0
D. 165.164.14.0 255.255.240.0
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Summarization is the process of advertising a network with a subnet mask such that it includes all of the subnets. For a simple example if you had two Class C networks, you could advertise them as a Class B network and it would encompass them both. Normally summarization should be implemented such that it summarizes ONLY the networks desired and no others (in the simple example it would possibly include other Class C networks). The process for arriving at the “best” summarization is a follows.
First, write the last octet that all networks share in common (third octet in this case) in binary form for each network:
165.164.8.0–00001000 165.164.10.0–00001010 165.164.12.0–00001100 165.164.14.0–00001110
The addresses have the first five bits in common; therefore, they can be summarized with the third octet 00001000 and a subnet mask of 255.255.248.0.
Another way of looking at it is that 165.164.8.0 255.255.248.0 covers the range of 165.164.8.0 through 165.164.15.255, the same range as all the component subnets.
None of the following possible answers is a valid range, nor do most of them cover the correct range of addresses:
165.164.8.0 255.255.240.0 is not a valid range. A 20-bit mask can only be on a subnet that is a multiple of 16, such as .16.0, .32.0, .48.0 etc. The subnet .8.0 is not a multiple of 16.
165.164.10.0 255.255.252.0 is not valid. A 22-bit mask requires a multiple of 4 in the third octet, and 10 is not a multiple of four. Even if it were a valid range, it does not cover the entire range of addresses that need to be summarized.
165.164.14.0 255.255.240.0 is not valid. The 20-bit mask is only usable on ranges that are multiples of 16 in the third octet, and 14 is not a multiple of 16. Even if the mask were valid, it could not cover the correct addresses.
When addresses are summarized the cost of the summary address will the highest cost of the component subnets. For example, in the partial sample output of the show ip route command below, there are three routes. The output is from a router running OSPFv3, so the addresses are IPv6, but the concept is the same.
OI 2001:0D B 8:0:0:7/64 [110/20]
via FE 80::A8BB:CCFF:FE 00:6F00, FastEthernet0/0
OI 2001:0D B 8:0:0:8/64 [110/100]
via FE 80::A8BB:CCFF:FE 00:6F00, FastEthernet0/0
OI 2001:0D B 8:0:0:9/64 [110/40]
via FE 80::A8BB:CCFF:FE 00:6F00, FastEthernet0/0
The routes have metrics (the second value in brackets, [administrative distance/cost]) of 20, 100, and 40. Therefore, the metric for the summarized route would be 100.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify manual and autosummarization with any routing protocol
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP Routing > Technology > Information Technology > White Papers > OSPF Design Guide
Question 2:
Refer to the exhibit. The AP status from Cisco DNA Center Assurance Dashboard shows some physical connectivity issues from access switch interface G1/0/14.
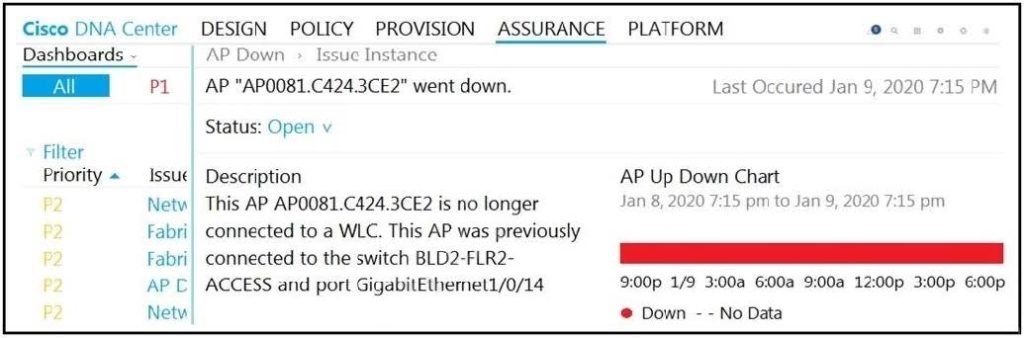
Which command generates the diagnostic data to resolve the physical connectivity issues?
A. check cable-diagnostics tdr interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
B. verify cable-diagnostics tdr interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
C. show cable-diagnostics tdr interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
D. test cable-diagnostics tdr interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
The Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) feature allows you to determine if a cable is OPEN or SHORT when it is at fault.
To start the TDR test, perform this task:
Step 1 (Starts the TDRtest):test cable-diagnostics tdr{interface{interface-number}} Step 2 (Displays the TDR test counter information):show cable-diagnostics tdr{interfaceinterface-number}

Question 3:
With respect to modifying an OSPF router ID to a loopback address, which of the following statements are true?
A. OSPF is not as reliable if a loopback interface is configured.
B. Using a loopback address avoids wasting an additional IP address.
C. A loopback interface is not always active, and it can go “down” like a real interface.
D. The loopback address does not automatically appear in the routing table of neighboring OSPF routers, so it cannot be pinged from other routers unless you include it with a network statement on the router local to the loopback interface.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
A loopback address does not automatically appear in neighboring routers\’ routing tables, so it cannot be pinged for network troubleshooting.
A work-around for this problem is to add a network statement under OSPF that advertises the loopback address network so that other routers will know how to reach your loopback.
A loopback address is an IP address assigned to a loopback interface, which is a logical interface on a router that behaves like a physical interface. Their advantage is that, unlike physical interfaces, logical interfaces do not go down.
For example:
Router(config)# interface loopback 0
Router(config-if)# ip address 172.17.1.1 255.255.255.0
In the example, a loopback IP address is used by OSPF to provide its router ID. This type of address is preferred because it is assumed to be more stable than a router ID tied to a physical interface. The traditional problem with a router ID
tied to a physical interface is that if the physical interface were to go down, the router would have to change its router ID to some other value. That would cause the OSPF neighbor relationships to reset and change values in the link-state
advertisements (LSAs), causing a disruption to the OSPF area.
With this consideration in mind, OSPF is more reliable when using a loopback interface than using a physical interface.
Using a loopback address does not avoid wasting an additional IP address. The address must still be unique.
A loopback interface is always active, and it cannot go “down” as a physical interface can.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify OSPF operations
References:
Cisco > IP Routing: OSPF Configuration Guide > Configuring OSPF > Forcing the Router ID Choice with a Loopback Interface
Question 4:
Refer to the exhibit.
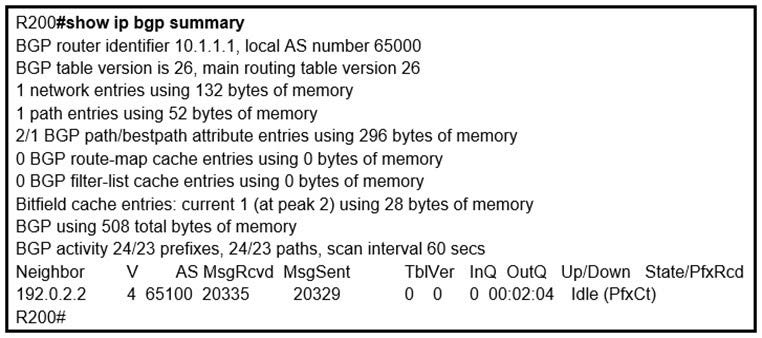
In which circumstance does the BGP neighbor remain in the idle condition?
A. if prefixes are not received from the BGP peer
B. if prefixes reach the maximum limit
C. if a prefix list is applied on the inbound direction
D. if prefixes exceed the maximum limit
Correct Answer: D
Question 5:
Company A recently acquired Company B and the network infrastructures are being merged. Both organizations used non-overlapping globally unique network addressing but different Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs). Initially, multiple WAN links will connect the two organizations. Company A will maintain its core routing protocol, and Company B\’s routing protocol will be the edge routing protocol. Two-way redistribution will be used to ensure full network routing capability.
What additional routing configuration should be performed to prevent routing loops and suboptimal routing?
A. Manually configure static routes.
B. Manually configure default routes.
C. Manually adjust the administrative distances.
D. Manually adjust the local preference attribute.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
When routes are being redistributed from the core into the edge and from the edge into the core, the administrative distance (AD) associated with external routes should be modified. This lessens the possibility of sub-optimal routing when multiple routing protocols advertise different paths to the same network.
The AD associated with the externally advertised routes should be higher than the internal IGP\’s AD. To change the AD for an entire routing protocol, use the distance command. An example and the command syntax are shown below:
router(config)#router rip
router(config-router)#distance 125
The complete syntax of the distance command is:
distance weight [address mask [ access-list-number | name]
The weight parameter is the AD, which can be a number from 10 to 255. Note that distances 0 through 9 are reserved for system use.
To change only the AD for selected networks, use an access list with the distance command as shown below:
router(config)# access-list 5 permit 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
router(config)# access-list 5 permit 11.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
router(config)# access-list 5 permit 12.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
router(config)# router rip
router(config-router)# distance 220 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 5
The 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 portion included with the distance command could hold an address/mask combination for a single address, but it is more common to use an access list.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify redistribution between any routing protocols or routing sources
References:
Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: Protocol-Independent Command Reference > distance (ip) Cisco > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > What Is Administrative Distance? > Document ID: 26634
Question 6:
Refer to the exhibit.
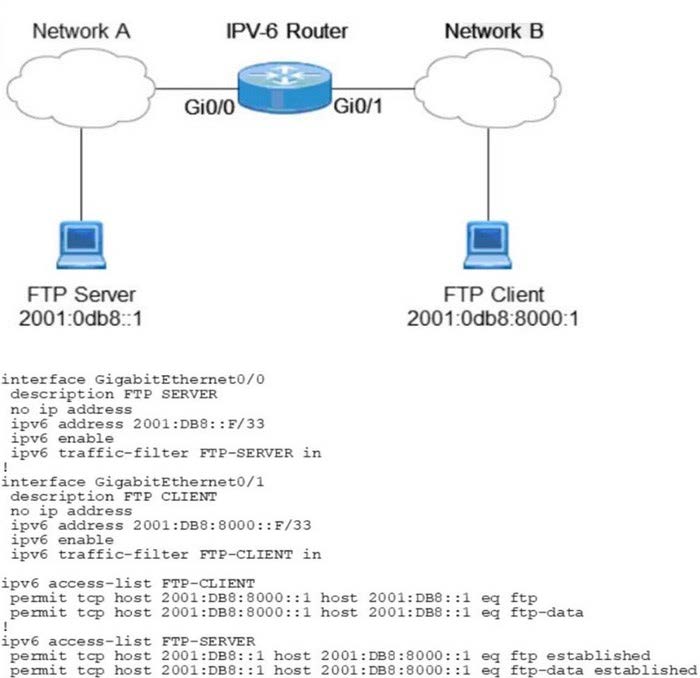
When an FTP client attempts to use passive FTP to connect to the FTP server, the file transfers fail Which action resolves the issue?
A. Configure active FTP traffic.
B. Modify FTP-SERVER access list to remove established at the end.
C. Modify traffic filter FTP-SERVER in to the outbound direction.
D. Configure to permit TCP ports higher than 1023.
Correct Answer: D
https://community.cisco.com/t5/switching/ftp-and-access-lists/td-p/1525257
Question 7:
You have been alerted that TCP traffic leaving an interface has been reduced to near zero, while UDP traffic is steadily increasing at the same time.
What is this behavior called and what causes it?
A. jitter, caused by lack of QoS
B. latency, caused by the MTU
C. starvation, caused improper configuration of QoS queues
D. windowing, caused by network congestion
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
This behavior is called starvation and is caused by improper configuration of QoS queues. When TCP and UDP flows are assigned to the same QoS queue, they compete with one another.
This is not a fair competition because the TCP packets will react to packet drops by throttling back TCP traffic, while UDP packets are oblivious to drops and will take up the slack created by the diminishing TCP traffic. The results from mixing UDP and TCP traffic in the same queue are:
Starvation
Latency
Lower throughput
While it is true that jitter can be caused by a lack of QoS, jitter is not what is being described in the scenario. Jitter is the variation in latency as measured in the variability over time of the packet latency across a network.
This phenomenon seriously impacts time-sensitive traffic, such as VoIP, and can be prevented by placing this traffic in a high-priority QoS queue.
While latency can be caused by the maximum transmission unit (MTU) in the network, this is not a case of latency, although latency may be one of the perceived effects of starvation. Latency is the delay in reception of packets. The MTU is the largest packet size allowed to be transmitted, and an MTU that is set too large can result in latency.
While windowing can be caused by network congestion, this is not a case of windowing. This is a technique used to adjust the number of packets that can acknowledged at once by a receiving computer in a transmission. In times of congestion the window, or number of packets that can be acknowledged at a time, will be small. Later, when congestion goes down, the window size can be increased.
Objective:
Network Principles
Sub-Objective:
Describe UDP operations
References:
Design Guide > Service Provider Quality of Service > CE Guidelines for Collapsing Enterprise Classes > Mixing TCP with UDP
Question 8:
Which is statement about IPv6 inspection is true?
A. It teams and secures bindings for stateless autoconfiguration addresses in Layer 3 neighbor tables
B. It learns and secures bindings for stateful autoconfiguration addresses in Layer 3 neighbor tables
C. It teams and secures bindings for stateful autoconfiguration addresses in Layer 2 neighbor tables
D. It team and secures binding for stateless autoconfiguration addresses in Layer 2 neighbor tables.
Correct Answer: D
Question 9:
An associate of yours configured a PPPoE connection. You have been alerted by a vulnerability tester that by using a sniffer, he was able to learn the connection credentials.
What type of authentication must your associate have configured on the connection?
A. PAP
B. 802.1x
C. CHAP
D. IPsec
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
The method used must have been Password Authentication Protocol (PAP). This method transmits the credentials in clear text, which makes it a poor choice.
There are only two methods available to authenticate a PPP connection, PAP and Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). CHAP never sends the password across the link. Rather, the authenticating end of the connection sends random text and other information to the requester.
The requester encrypts this data with its password and sends it back. The authenticating end of the connection reverses the encryption using the same password and compares the result with what was originally sent. If it matches, the authenticating end of the connection is assured that the requesting end knows the password.
The connection could not have used either 802.1x or IPsec, as neither method would transmit the credentials in clear text.
The connection could not have used CHAP. If it had, the credentials could not have been captured with a sniffer.
Objective:
Layer 2 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify PPP
References:
Cisco > Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15MandT > Configuring Authentication > Non-AAA Authentication Methods > Enabling CHAP or PAP Authentication Cisco > Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15MandT (PDF)
Question 10:
Refer to the exhibit.

R1 cannot authenticate via TACACS
Which configuration resolves the issue?
A. aaa group server tacacs+ DC1_TACACS server name DC_TACACS
B. tacacs server DC1_TACACS address ipv4 10.66.66.66 key D@t@c3nter1TACACS
C. tacacs server DC1_TACACS address ipv4 10.60.66.66 key D@t@c3nter1TACACS
D. aaa group server tacacs+ DC_TACACS server name DC_TACACS
Correct Answer: B
Question 11:
View the sample output of the debug ip eigrp command.

What is the significance of the number 4294967295 as shown in the output?
A. It represents the unreachable metric for EIGRP.
B. It represents the administrative distance for EIGRP.
C. It represents a reachable metric for the given network.
D. It represents one of the link characteristics that EIGRP uses to calculate the metric.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
The value 4294967295 in the debug ip eigrp output represents the unreachable metric for EIGRP. This means that the network has become unavailable and cannot be reached. In this output, the M represents the local metric, and the SM represents the metric that was reported by the neighbor that advertised the network to the local router.
The administrative distance (AD) for internal EIGRP is 90.
The link characteristics that are used in the EIGRP calculation are shown following the dash after the M and SM values (1657856 4294967295). By default, EIGRP only uses bandwidth and delay in its calculation.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe and optimize EIGRP metrics
References:
Cisco > Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference > debug h225 asn1 through debug ip ftp > debug ip eigrp
Question 12:
An engineer configured policy-based routing for a destination IP address that does not exist in the routing table. How is the packet treated through the policy for configuring the set ip default next-hop command?
A. Packets are not forwarded to the specific next hop.
B. Packets are forwarded based on the routing table.
C. Packets are forwarded based on a static route.
D. Packets are forwarded to the specific next hop.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
The set ip default next-hop command verifies the existence of the destination IP address in the routing table, and…+ if the destination IP address exists, the command does not policy route the packet, but forwards the packet based on the routing table.+ if the destination IP address does not exist, the command policy routes the packet by sending it to the specified next hop.
Question 13:
Consider the following diagram. All PVCs are active.
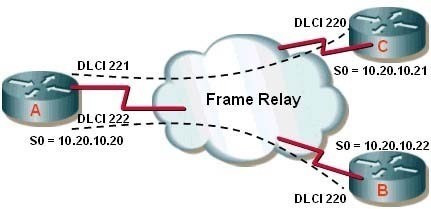
If the partial output of the show ip ospf neighbor command executed on Router A is as follows, which of the following statements is TRUE?
RouterA# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
1.1.1.1
1 FULL/DROTHER 00:00:13 10.20.10.21 SerialO
2.2.2.2
1 FULL/DR 00:00:51 10.20.10.22 SerialO
A. Router C and Router B will fail to have all OSPF routes in their tables.
B. All routing tables will be populated correctly.
C. Router A will be the DR.
D. Router C will be the DR.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
The output of the command shows that Router C and Router B will fail to have all OSPF routes in their tables. In a hub and spoke configuration, as depicted in the diagram, the hub router (Router A) should be the designated router (DR) or the source of updates to the other routers.
However, Router B is the DR, as evidenced by the output of the show ip ospf neighbor command executed on Router A. This situation could be rectified by setting Routers B and C with a priority of 0, which would disqualify them from being the DR. After that, all routes could be distributed from the hub, which would have visibility of all routes.
All routing tables will be populated correctly until the hub router is made the DR.
Neither Router A nor C will be the DR, since it is indicated that Router B is the DR in the output of the command.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify OSPF operations
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Support Technology > Support > IP Routing > Configure > Configuration Examples and Technotes > Initial Configurations for OSPF over Frame Relay Subinterfaces Cisco > Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking
Command Reference > frame-relay lapf n201 through fr-atm connect dlci > frame-relay map
Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference > ip ospf network
Question 14:
Refer to the exhibit.
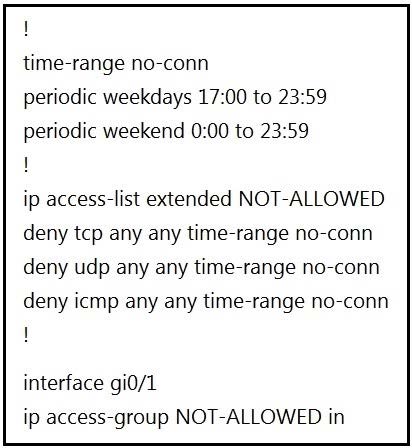
A network administrator wants to block all traffic toward the Internet after business hours and on weekends. When the administrator applies an access list on interface Gi0/1, all traffic is blocked and there is no access to the Internet at any time.
Which action resolves the issue?
A. Add the permit ip any any time-range no-conn statement after the deny udp any any time-range no-conn command in the access list.
B. Add the permit ip any any statement after the deny icmp any any time-range no-conn command in the access list.
C. Add the permit allowed time-range no-conn statement after the deny icmp any any time-range no-conn command in the access list.
D. Add the permit ip any any time-range no-conn statement after the deny icmp any any time-range no-conn command in the access list.
Correct Answer: B
Question 15:
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two actions should be taken to access the server? (Choose two.)
A. Modify the access list to add a second line of permit ip any
B. Modify the access list to deny the route to 192.168.2.2.
C. Modify distribute list seq 10 to permit the route to 192.168.2.2.
D. Add a sequence 20 in the route map to permit access list 1.
E. Add a floating static route to reach to 192.168.2.2 with administrative distance higher than OSPF
Correct Answer: BE
……
2025–2026 CCNP Enterprise Market Outlook
In 2025, enterprise networks continue migrating to multi-cloud, software-defined WAN, and advanced segmentation. The ENARSI certification remains highly respected, especially for roles such as:
- Enterprise Network Engineer
- Routing & Switching Specialist
- SD-WAN Support Engineer
- Infrastructure Operations Engineer
Between 2025 and 2026, Gartner forecasts rising demand for engineers skilled in hybrid networking and automation, directly reinforcing the value of the 300-410 certification.
Latest Insights from Cisco Community & Industry Experts
Community feedback in late 2025 indicates:
- Troubleshooting questions feel more realistic
- VPN and BGP configuration scenarios appear more frequently
- Candidates who lab daily have significantly higher pass rates
Senior engineers also observe growing emphasis on programmability, signaling future CCNP evolution.
Additional Study Resources for the 300-410 Exam
Consider integrating resources like:
- Cisco Learning Network (official learning hub)
- Cisco Press ENARSI guides
- EVE-NG, GNS3, CML for labs
- https://www.dumpsdemo.com/category/best-cisco-exam-questions-and-answers/ccnp/
Common Mistakes Candidates Should Avoid
Avoid outdated materials—anything before 2024 is too old for today’s blueprint.Finally, avoid skipping Cisco’s official documentation; it’s the backbone of understanding.
Final Recommendation – Maximize Your Chances of Passing
Combining updated Leads4pass dumps, hands-on lab practice, and official documentation gives you the strongest chance of success. The updated 955-Q&A collection remains one of the most trusted resources for 300-410 candidates in 2025.
👉 Access Updated 300-410 Dumps
Conclusion
With Cisco’s 2025 updates emphasizing troubleshooting, VPN technologies, and realistic network operations, the 300-410 exam remains one of the most important certifications for enterprise networking professionals heading into 2026. Updated practice questions and well-structured study paths can dramatically boost your confidence—and Leads4pass offers one of the most consistently reliable resources available.
FAQs
1. Are the 300-410 exam topics expected to change again in 2026?
Minor enhancements are likely as Cisco increases focus on automation.
2. Is the 300-410 ENARSI exam difficult?
It is challenging, especially for those weak in troubleshooting or VPN configuration.
3. Are dumps enough to pass the exam?
They help but should be combined with labs and Cisco documentation.
4. How long should I study for the 300-410 exam?
Most candidates prepare for 2–3 months depending on experience.
5. Is Leads4pass a reliable source for updated dumps?
Yes, their updates typically match the latest exam patterns.